Story By Caribborida Ganjier; Roddrick Taylor Certified Ganjier
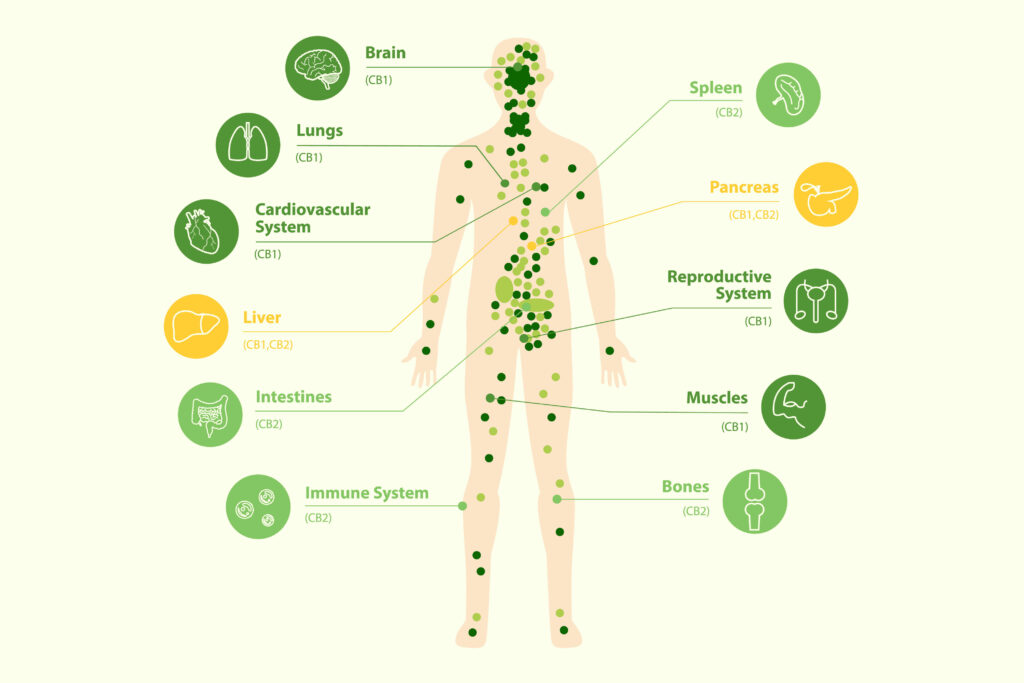
In Parts one and two of What We Know About The Human Endocannabinoid System, we explored the CB1, CB2 receptors and the G proteins that are coupled with them. We discussed location and functionality of these receptors, well as much as we know. We want to continue with other components that help with the regulation or homeostasis of the human body. Endocannabinoids. Yes, the human body has cannabinoids inside. These cannabinoids are referred to as endocannabinoids. Endocannabinoids either block or deliver a path of relief to what is bothering us in our central nervous system and immune systems.
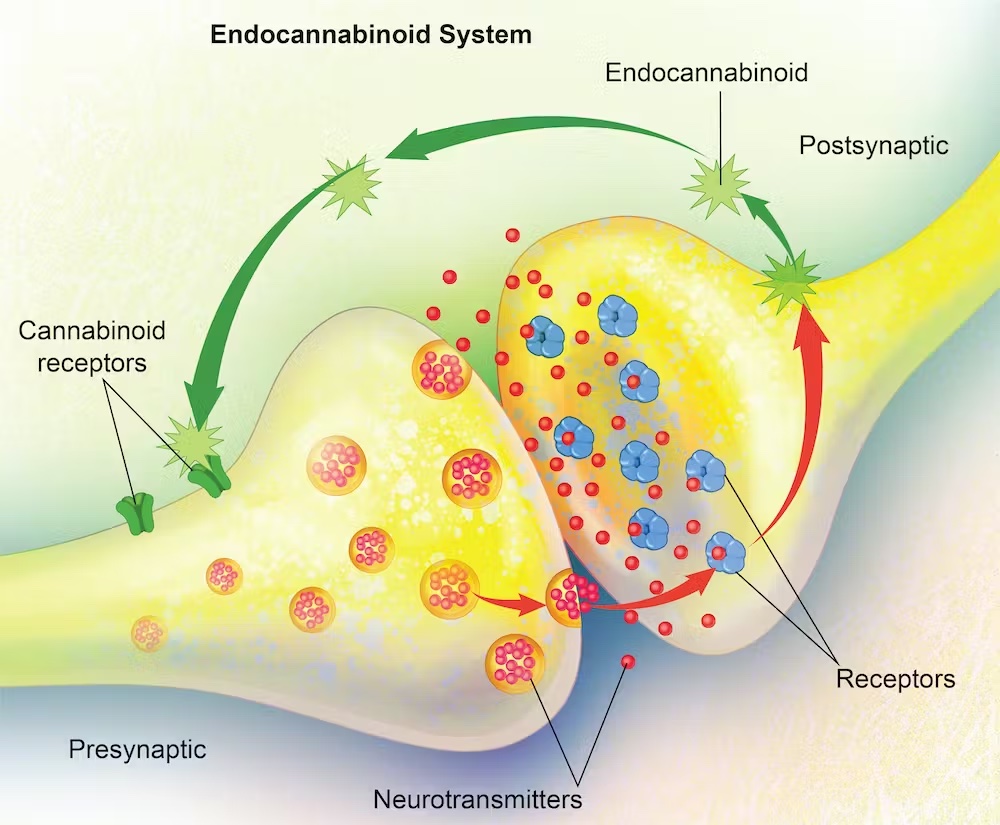
Endocannabinoids are a class of signaling molecules naturally produced by the human body (and other animals) that interact with the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system is a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including pain sensation, mood, appetite, immune function, and more. It helps maintain homeostasis, which is the body’s internal balance.
There are two primary endocannabinoids identified in humans:
- Anandamide (AEA): Anandamide is derived from the Sanskrit word “ananda,” meaning bliss or happiness. It is produced on-demand in response to various physiological stimuli. Anandamide binds to cannabinoid receptors, particularly the CB1 receptor found in the brain and central nervous system, where it plays a role in regulating mood, appetite, and pain perception.
- 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG): 2-AG is the other major endocannabinoid. It is also produced as needed and mainly interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, influencing immune function, inflammation, and other processes.
The functions of endocannabinoids within the human body are diverse and complex. Some of their roles include:
- Regulating Pain: Endocannabinoids can modulate pain perception and help to reduce pain and inflammation when necessary.
- Mood and Emotion Regulation: The endocannabinoid system is involved in mood regulation, stress response, and emotional well-being. This is why it has been implicated in conditions such as anxiety and depression.
- Appetite Control: Endocannabinoids influence appetite and metabolism, which is why they have been explored in the context of obesity and eating disorders.
- Immune Function: The endocannabinoid system plays a role in regulating the immune response, which can have implications for autoimmune diseases and inflammatory conditions.
- Neuroprotection: Some studies suggest that endocannabinoids may play a role in protecting the nervous system and brain cells.
- Regulating Sleep: The endocannabinoid system has been linked to the regulation of sleep, which is why it’s also relevant in the context of sleep disorders.
- Fertility and Reproduction: Endocannabinoids have been found to influence fertility and reproduction processes.
It’s important to note that the endocannabinoid system is a complex and relatively newly discovered system, and research into its functions and the potential therapeutic applications of endocannabinoids is ongoing. Furthermore, the interaction between endocannabinoids and the phytocannabinoids found in the cannabis plant (e.g., THC and CBD) has also generated significant interest and research due to the potential medical benefits and psychoactive effects associated with cannabis use. Stay in the know by subscribing to Cannabisquery.com.

