By Caribborida Ganjier; Roddrick Taylor Certified Ganjier
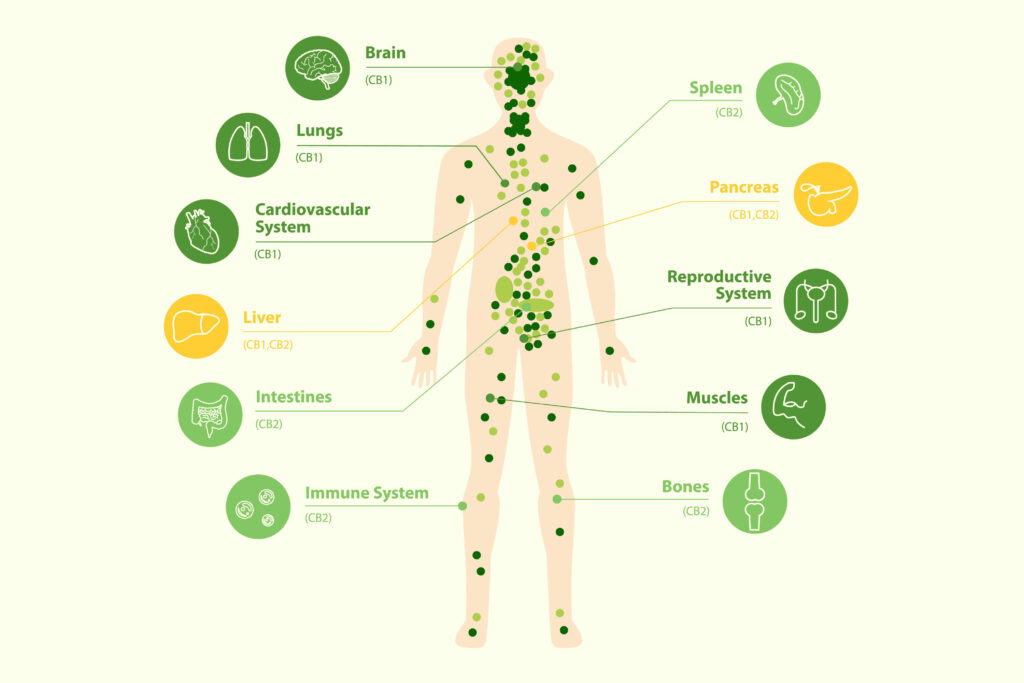
In part one of What We Know About The Endocannabinoid System: Regulators Mount Up, we discussed our CB1 and CB2 receptors and their primary functions. The endocannabinoid system also couples with some known G proteins; which are placed throughout the body. G proteins are paired with our CB1, CB2 receptors, and act as mediators for endocannabinoids to bring the balance needed. It is believed that CBD and THC do stimulate some of these G protein receptors but it has not been proven.
Here’s a brief overview of their potential functions:
- GPR18: GPR18 is a G protein-coupled receptor that was thought to be involved in the endocannabinoid system. GPR18 is directly connected to bone marrow, reproductive system, and immune system. It may play a role in immune function and inflammation regulation, but its exact functions are still being explored at that time.
- GPR119: GPR119 is another G protein-coupled receptor that is potentially linked to the endocannabinoid system. GPR119 is directly connected to the digestive tract and the pancreas. It’s primarily associated with glucose homeostasis and insulin release, suggesting a role in metabolic regulation.
- TRPV1: The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor is involved in pain perception and temperature regulation. TRPV1 is directly connected to the brain, bone marrow, muscle cells, thyroid gland, liver, digestive tract, kidneys, bladder, reproductive system, fat cells and skin. While it’s not a direct part of the endocannabinoid system, it can be influenced by endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (like capsaicin found in chili peppers). This receptor plays a role in pain modulation and inflammatory responses.
- GPR55: GPR55 is another G protein-coupled receptor that was initially thought to be part of the endocannabinoid system. GPR55 is directly connected to brain, bone marrow, immune system, reproductive system, bladder and intestine. Its precise function is not fully understood, but it has been associated with various processes, including modulation of cell proliferation, bone health, and potential roles in certain diseases.
We have provided you with an overview of the CB1, CB2 receptors; as well as their known coupled G proteins. In parts three and four, well will touch on the endocannabinoids and enzymes that are the remaining components of the human endocannabinoid system. It’s important to note that our understanding of these receptors and their roles in the endocannabinoid system are evolving. As new information evolves on the endocannabinoid system, we at Cannabisquery.com will bring you updates.

